Plants are fascinating organisms that possess various adaptations to overcome environmental challenges. One such adaptation is the ability to store nutrients and water in specialized structures such as tubers.
Tubers are modified plant structures that store carbohydrates and other nutrients to help plants survive harsh conditions like drought, extreme temperatures, or winter.
There are two main types of tubers: stem tubers and root tubers. Stem tubers grow from the stem while root tubers grow from the roots. Both are storage systems of the plant and play a vital role in its survival.
Characteristics of Stem Tubers
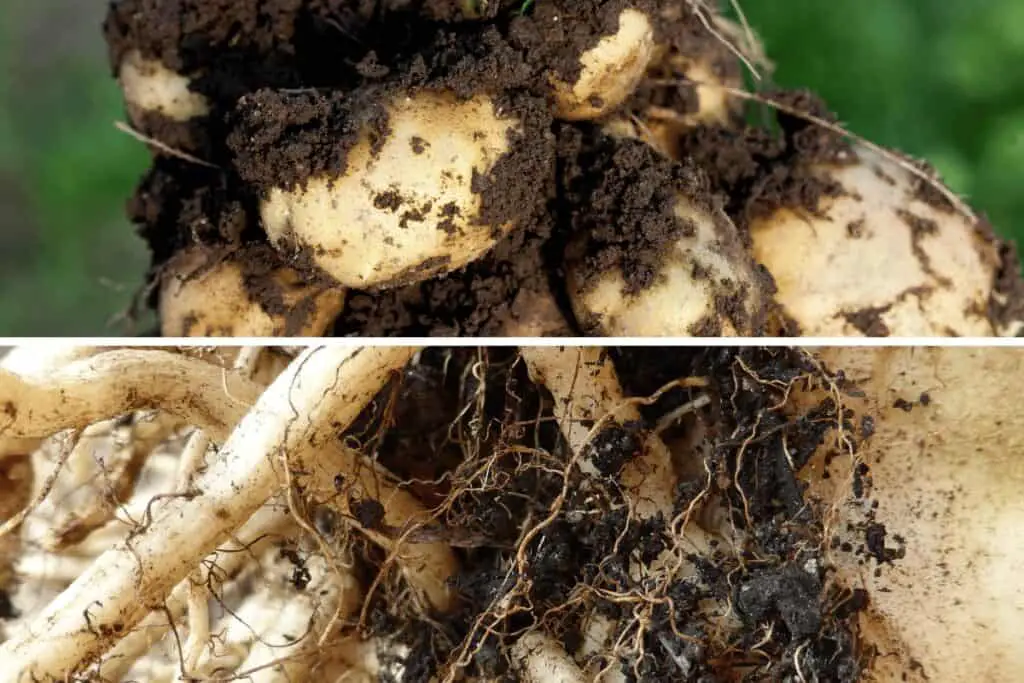

[1] Stem tubers are swollen, fleshy underground stems that store carbohydrates, water, and other nutrients. They grow next-generation plants from the flesh of the tuber itself.
Stem tubers can start with a node and eventually produce a vertical stem and leaves. Roots then sprout from the underside of the stem. Stem tubers have eyes or nodes on them that can produce new shoots.
The eyes often begin to sprout into new shoots when left for some time. A great example of stem tubers is the potato tuber.
Characteristics of Root Tubers
[3] Root tubers, on the other hand, are swollen roots that store food and water. They are also known as storage roots. Root tubers are formed by the thickening of the roots, which results in a fleshy mass.
The roots are modified to store nutrients and water during the growing season for use during periods of dormancy or stress. Some examples of plants that produce root tubers include sweet potato, yam, and cassava.
Similarities and Differences Between Stem and Root Tubers
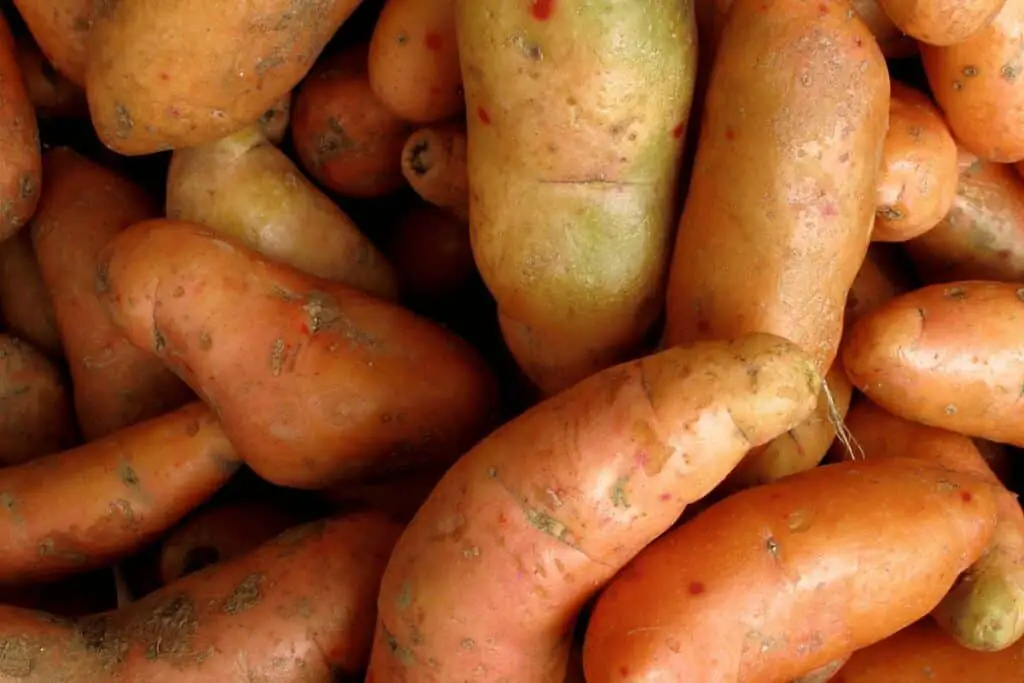
[2] Stem and root tubers have many similarities and differences. For example:
Similarities
- Both stem and root tubers are storage organs that store nutrients and water to help plants survive harsh conditions.
- Both stem and root tubers can produce new plants
- Both types of tubers are underground structures
Differences
- Stem tubers have eyes or nodes that produce new shoots, while root tubers don’t have nodes
- Root tubers are modified roots, while stem tubers are modified stems
FAQs
What is the importance of stem tubers and root tubers?
Stem tubers and root tubers are essential to plant storage systems that allow plants to survive harsh environmental conditions. They store nutrients and water that plants can use during periods of dormancy or stress. They also play a significant role in vegetative propagation, allowing plants to reproduce.
What is the difference between stem tubers and root tubers?
Stem tubers and root tubers are both types of modified plant structures used for food storage, but they differ in their origin and anatomy. Root tubers represent swollen roots and can arise from any part of the root system, while stem tubers develop from underground stems called rhizomes.
Stem tubers can store complex carbohydrates like starch, while root tubers can store simple carbohydrates like glucose. Stem tubers can give rise to many tubers, while only a single tuber is produced by root tubers.
Stem tubers also have apical buds, scaly leaves, and auxiliary buds, which are absent in root tubers [1][2].
What are stem tubers and root tubers examples?
What are 5 examples of stem tubers?
Is a potato a root or stem tuber?
Potato is a stem tuber, which means that it is a modified underground stem that stores nutrients and energy. Potatoes grow on the stolons or runners of the potato plant, which are thick, fleshy, and swollen structures that form from the base of the stem [2].
Conclusion
stem tubers and root tubers are two different types of modified underground structures that store nutrients and energy for plants. The main difference between them lies in the plant part that undergoes swelling, with stem tubers being swollen stems and root tubers being swollen roots [1].
Stem tubers possess several eyes that can develop into new plants, whereas root tubers can arise from any part of the root and have several finer root branches, but no eyes or axillary buds [2]. Stem tubers usually have scale leaves with axillary buds that can produce new plants, while root tubers are modified lateral roots enlarged to function as storage organs [3].
Examples of stem tubers include potatoes, yams, and sweet potatoes, while examples of root tubers include dahlias, sweet potato vine, and cassava. Understanding the differences between stem tubers and root tubers is important for horticulture and agriculture, as it can impact planting and cultivation techniques.
Latest Posts
- How to Plant Lettuce Seeds for Maximum Germination

- How to Plant Kale Seeds: A Step-by-Step Guide to Maximum Germination Success!

- How to Plant Eggplant Seeds: A Step-by-Step Guide to Maximum Germination Success!

- How to Plant Cucumber Seeds for Maximum Germination

- How to Plant Chili Pepper Seeds for Maximum Germination

- How to Plant Cabbage Seeds for Maximum Germination





